First and foremost, before placing a single penny on any trade in the CFD FX market, open a DEMO account, one of the key factors with any type of trading is the inherent risk associated with trading; so remove this risk, and educate yourself in a demo environment.
Buy (Long): You buy the currency pair if you anticipate that the base currency will appreciate (increase in value) relative to the quote currency. For instance, buying GBPUSD means purchasing British Pounds while selling US Dollars.
Sell (Short): You sell the currency pair if you expect the base currency to depreciate (decrease in value) relative to the quote currency. Selling GBPUSD involves selling British Pounds to acquire US Dollars.
Key Concepts:
Currency Pair: A currency pair represents the quotation of two different currencies, where one currency's value is stated in terms of the other.
Base Currency: The base currency is the first currency listed in a currency pair. It indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.
Quote Currency: Also known as the term currency, it is the second currency listed in a currency pair. It specifies the value of the base currency in terms of itself.
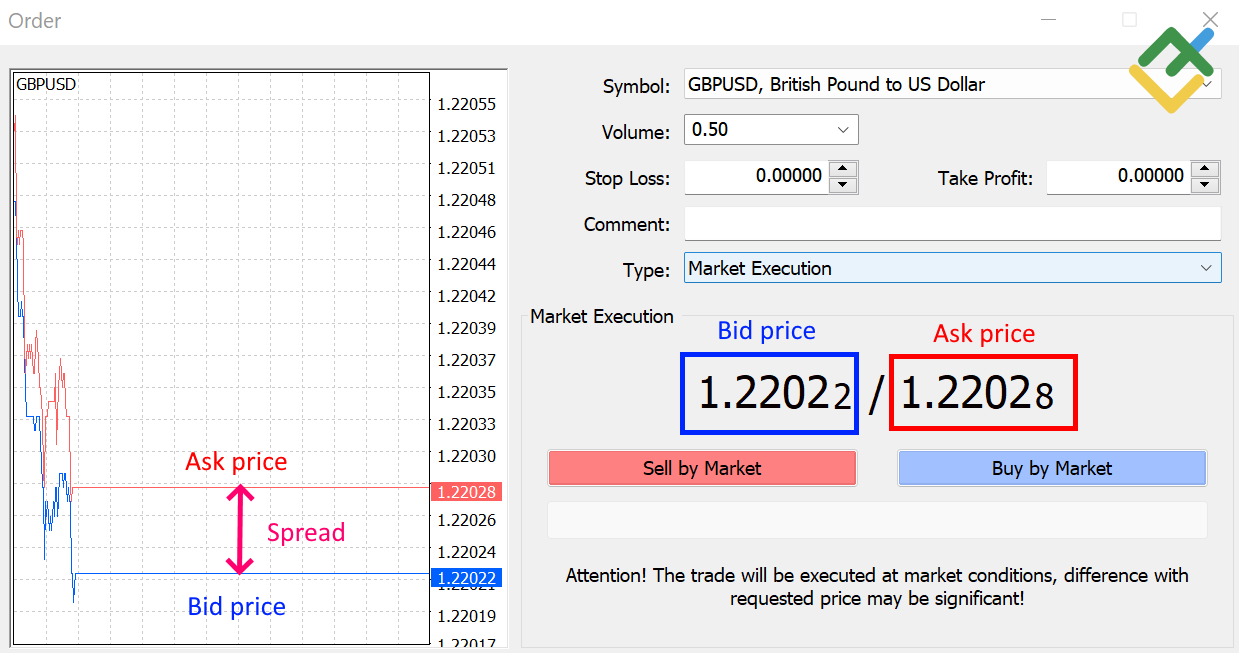
BID & ASK Prices:
Bid Price: This is the price at which the broker is willing to buy the base currency in exchange for the quote currency. Traders sell at the bid price.
Ask Price: This is the price at which the broker is willing to sell the base currency in exchange for the quote currency. Traders buy at the ask price.
Execution of Trades:
Buy Positions: These are initiated at the ask price (higher) and closed at the bid price (lower).
Sell Positions: These are opened at the bid price (lower) and closed at the ask price (higher).
You have decided on what currency pair you want to trade on and you have decided if you will buy or sell - how to determine your cost....
Spread and Pip Definition
Spread: Refers to the difference between the Bid and Ask prices quoted by brokers. It represents the cost incurred by traders when executing trades. For instance, if the Bid price for EURUSD is 0.99259 and the Ask price is 0.99267, the spread is 0.8 pips.
Pip: Stands for "percentage in point" or "price interest point". Most forex prices are quoted to 5 decimal places, where the fourth digit after the decimal represents one pip. For example, if EURUSD moves from 1.12345 to 1.12355, this denotes a change of 10 pips.
Trade Size and Lots
- Trade Size: Traders define the volume of their trades in terms of "Lots" or "Units". In forex platforms, trading volume is typically denominated in Lots. One standard Lot equals 100,000 units of the base currency of the traded pair. For instance, trading 1 Lot of EURUSD means speculating on €100,000 worth of currency.
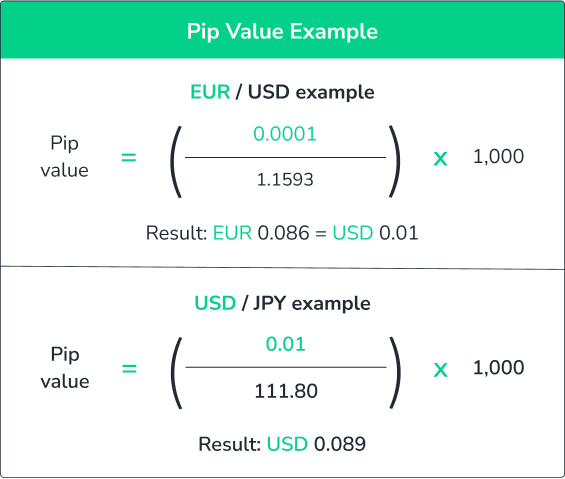
Pip Value Calculation
Pip Value: Determines the monetary value of a single pip movement in a currency pair. It's crucial for calculating potential profits or losses in trades. The pip value can be computed using the formula: Pip in decimals (0.0001) x Trade size in Units.
Examples:
- If you trade 0.5 Lots of EURUSD and the pip value is $5, a movement of 1 pip will result in a profit or loss of $5.
- Similarly, trading 0.5 Lots of EURGBP with a pip value of £5 means each pip movement will affect your profit or loss by £5.
Calculating Profit and Loss (P/L)
To calculate the Profit or Loss of a trade:
- Determine the pip value of the trade.
- Calculate the difference between the opening and closing prices in pips.
- Multiply the pip value by the number of pips difference to ascertain the total Profit or Loss.
Example Calculation:
- Scenario: You open a trade of 1 Lot on EURUSD at 1.99959 and close it at 1.99999.
- Calculation:
- Pip value = 0.0001 x 100,000 units = $10.
- Price movement = 1.99999 (closing price) - 1.99959 (opening price) = 4 pips.
- Profit/Loss = 4 pips x $10 (pip value) = $40.
Understanding these fundamental concepts is essential for navigating the forex market effectively, managing risk, and making informed trading decisions.


Comments
Post a Comment